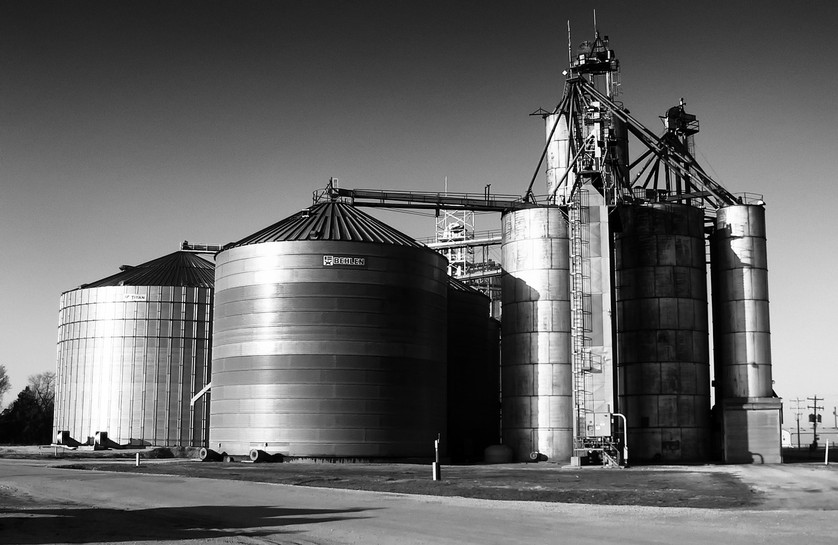
10 Tips for Protecting Your Grain Bins From Moisture
Every year, several billion metric tons of grain are produced around the world. Corn is the most popular type of grain, followed by wheat and milled rice. Barley, oats, and rye round out the top five crops most commonly stored in grain bins.
Because the demand for grain is so high, it's the top crop for many farmers. But that doesn't mean it's easy to produce. In addition to challenges during growing, there's a lot that needs to be carefully managed after harvesting.
Keeping moisture away from grain is the perfect example of this type of challenge. If moisture isn't carefully controlled, it can ruin part or all of a grain harvest.
Since dealing with moisture is such a big deal for anyone involved with farming grain, here are ten actionable tips for keeping it out of where grain is stored:
1. Give Grain Time to Dry
One of the biggest mistakes someone can make in regards to grain and moisture is not giving it enough time to dry after harvest. When grain is first harvested, it's still a live seed. That means insects and mold can still be present.
If grain is immediately stored, those pests will contaminate the storage area. Fortunately, allowing grain to dry after it's taken from the field will reduce the likelihood of those types of problems.
2. Sanitize
In addition to drying time, sanitizing should play a role before and during the harvest process. It's important to carefully inspect the area where the grain will be stored for any type of rodent presence.
Other important steps include keeping nearby vegetation cut and promptly cleaning up if any grain gets spilled. These measures will help keep the storage area in optimal condition.
3. Load Carefully
Minimizing broken kernels should be a top goal of any grain loading process. The same is true for removing foreign elements.
When grain isn't carefully loaded into bins, the initial quality is going to be lower. Broken kernels can also reduce aeration, which in turn will raise moisture and potentially lead to spoilage.
4. Ventilation
There are certain factors that increase humidity and encourage moisture. Then there are other factors that help to minimize moisture. Ventilation is definitely in the latter category.
Solid ventilation is an absolute must for keeping moisture out of grain bins. Whether it's natural or intentional ventilation, having a solution will keep hot air from creating moisture in the grain.
5. Aeration
Aeration is generally viewed as an important complement to ventilation. One main difference between the two is the frequency of when they're used. In most cases, bins should remain ventilated throughout the duration of grain storage.
But for aeration, this is typically a process that only needs to be done every few weeks. The ideal time for aeration is when it's cooler in the morning. Running this process for a few hours will really help control moisture.
6. Periodically Unload
As we've alluded to, the excess heat that accumulates in grain bins is part of why it can be such a challenge to control moisture. One way to address this issue is to periodically unload grain.
The reason this technique can work quite well is it gets rid of the top grain that's likely to be the warmest.
If you need help measuring how much grain you're moving during this process, a grain gauge bin level monitor will help you keep track of the current grain levels in your bin.
7. Understand Seasonality
Dealing with moisture can be even more of a challenge if you don't know exactly what you're up against. This is why it's so important to understand the target grain moisture content levels for the high temperatures of summer.
The lowest level is 11% for soybeans. The level jumps to 13% for grain sorghum. And it's 13.5% for both wheat and corn. Even though market moisture content can exceed these percentages, it's important to keep grains at those levels during storage.
In terms of checking these thresholds, be sure to take the impact of higher summer temperatures into account. You can simulate this by warming a sample of grain in a sealed bag prior to measuring.
8. Time Grain Bins Storage Correctly
The amount of time that grain can safely stay in storage depends on a combination of the temperature and moisture. A helpful rule of thumb is for every ten degrees of heat increase during storage, the amount of time is cut in half.
That translates into 240 days of storage at sixty degrees but less than 125 days if the temperature is at least seventy degrees. Just as a higher temperature reduces storage time, so does rising moisture levels inside grain bins.
Because keeping grain in storage for too long is a recipe for ruining it, be sure to factor in summer temperature fluctuations before picking your starting date for grain storage.
9. Monitor Target Temperatures
Even with the best plans and preparation, it's possible for the weather to throw a curveball while grain is in storage. A sudden change to the current grain moisture level or temperature will need to be addressed.
As far as how often you'll want to check, it really depends on the current temperature outside. During the peak heat of summer, it's well worth your time and energy to check your storage on a weekly basis.
10. Keep Detailed Records
Modern technology makes it easier than ever to collect lots of data while grain is in storage. All of this data can actually start to get overwhelming. You can avoid confusion or drowning in data by keeping detailed records.
Not only will these records help you with your current grain storage, but you can use what you learn as a baseline for future storage efforts.
Since total weight is one of the data points you will likely track, using an AgraTronix Test Weight Grain Scale is a great way to ensure you are getting consistent readings.
 US Dollars
US Dollars
 Canadian Dollar
Canadian Dollar
 Australian Dollar
Australian Dollar
 Euro
Euro

